-
3D printers
Back
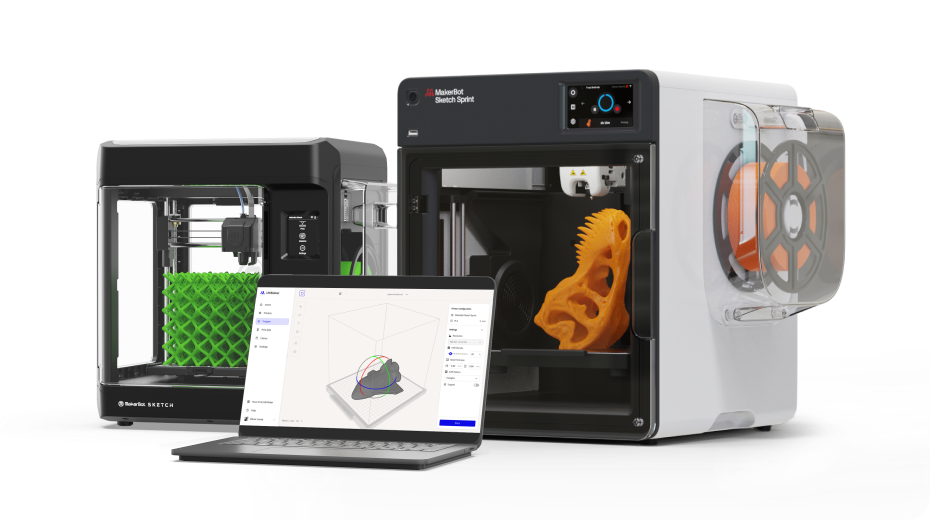
3D printers
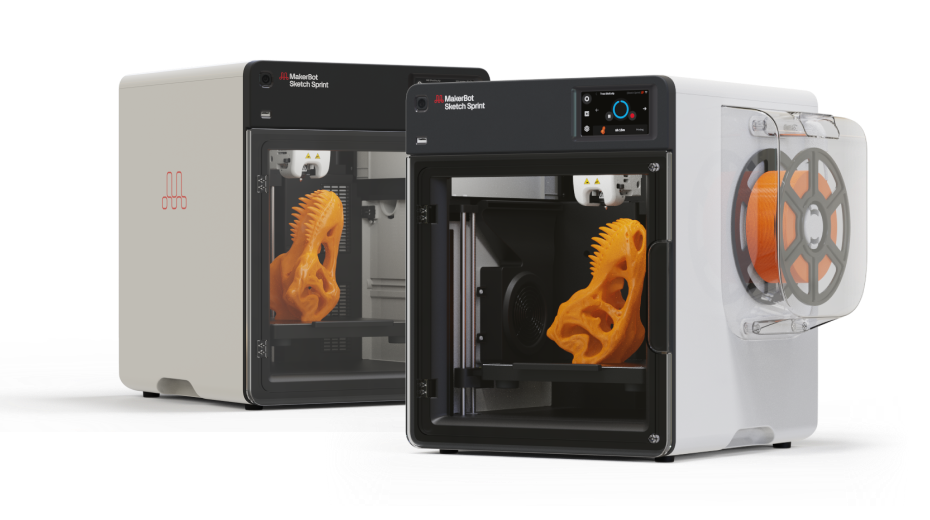
Upgrade your classroom with reliable 3D printers used across 10,000+ schools.
Meet the new Sprint -
Education
Back
Sketch Classroom Solution
3D printing in the classroom isn’t just about the 3D printer. It’s about the curriculum, the projects, and knowledge that surrounds it.
Classroom setupClassroom setup
Which Sketch Classroom configuration is right for you?
District Solution
From Classroom to District: Scale Your Educational Journey.
UltiMakerCare service plans
Service plans that support you throughout your 3D printing journey.
-
Software
Back
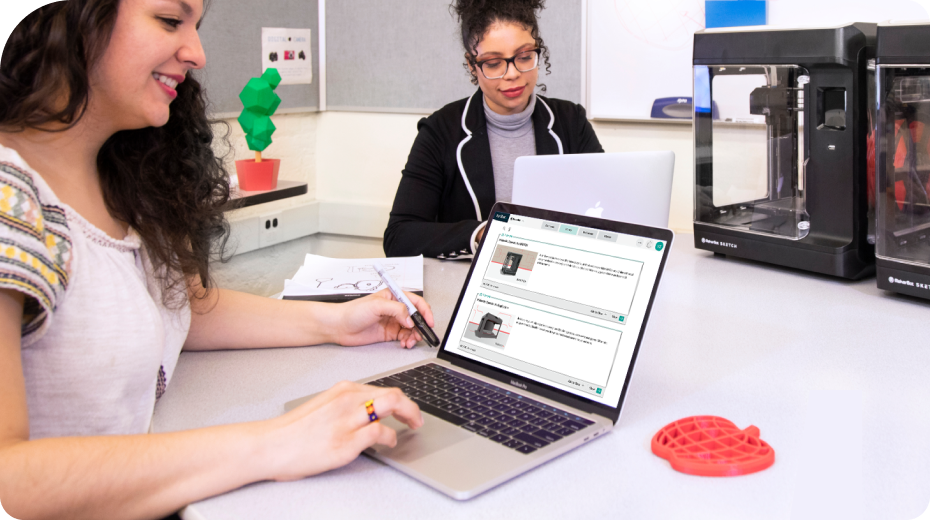
Teacher Tools to Help You Print
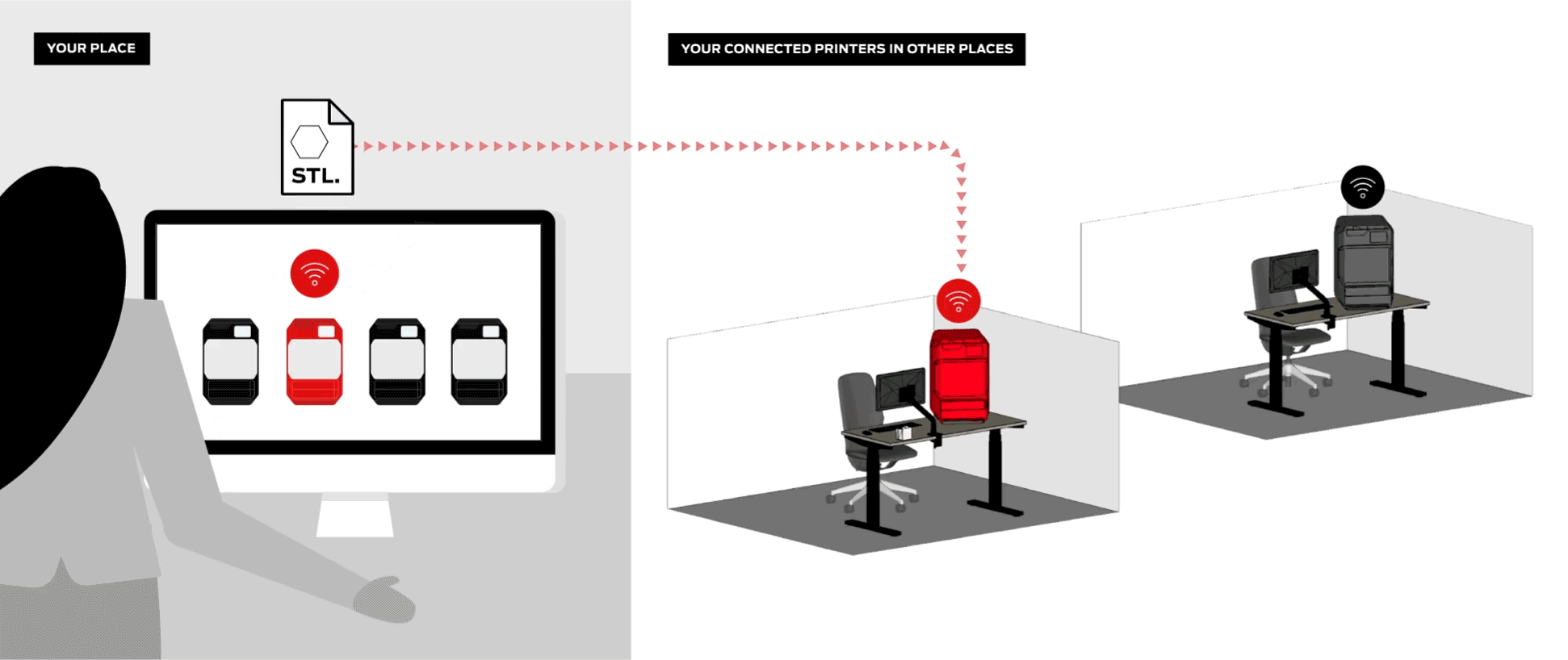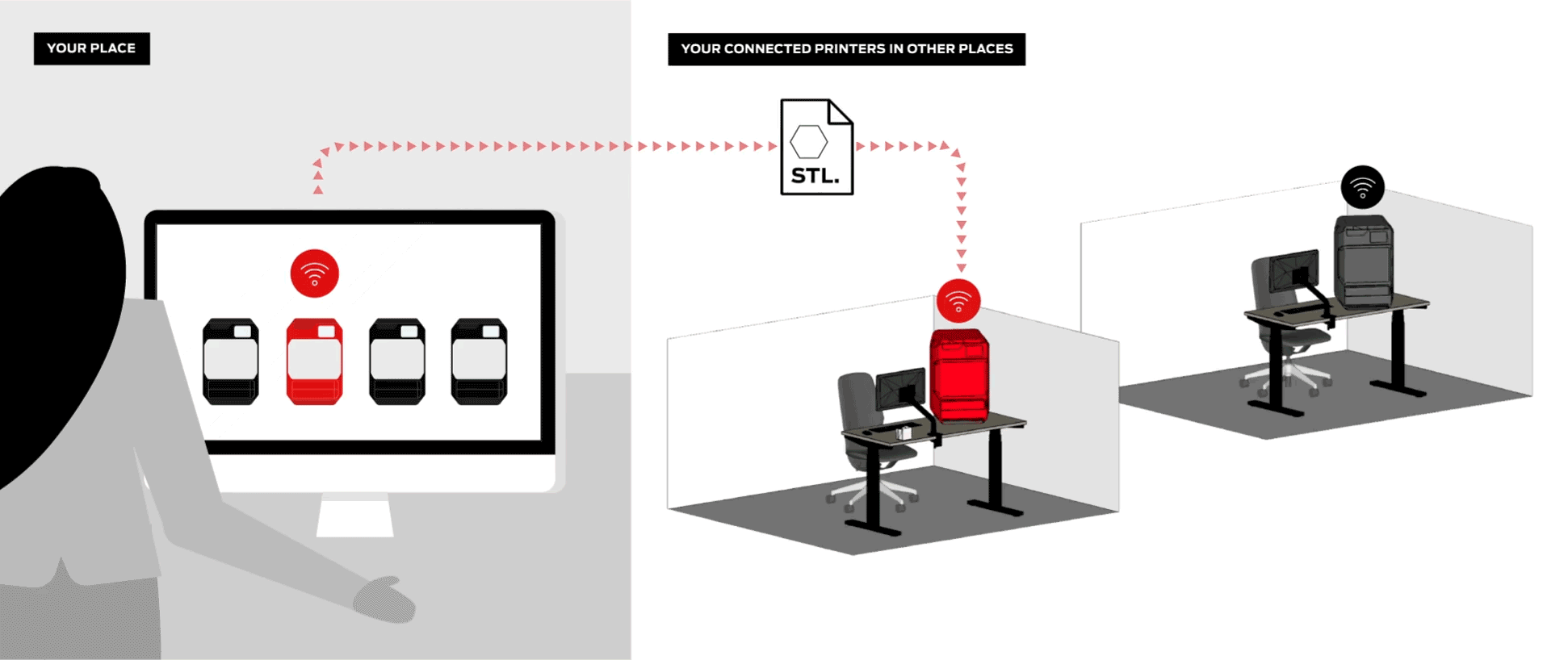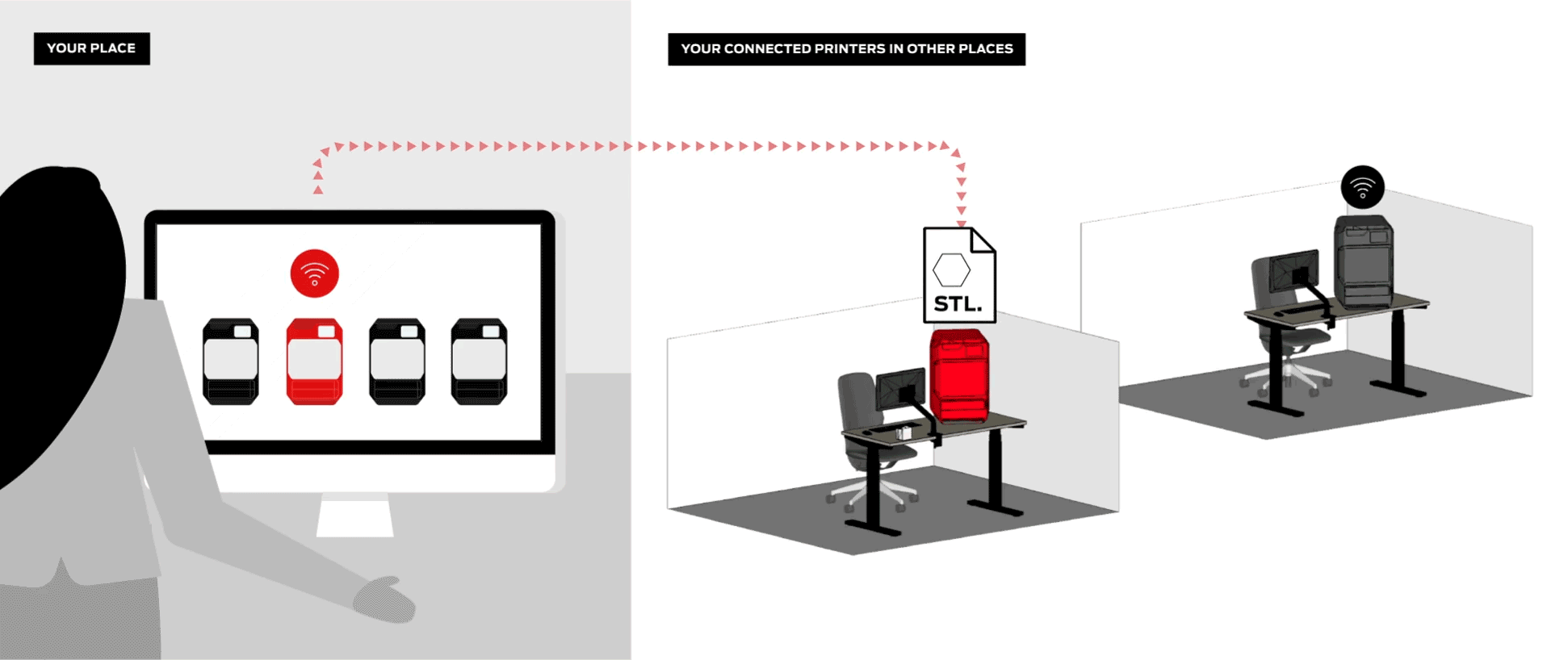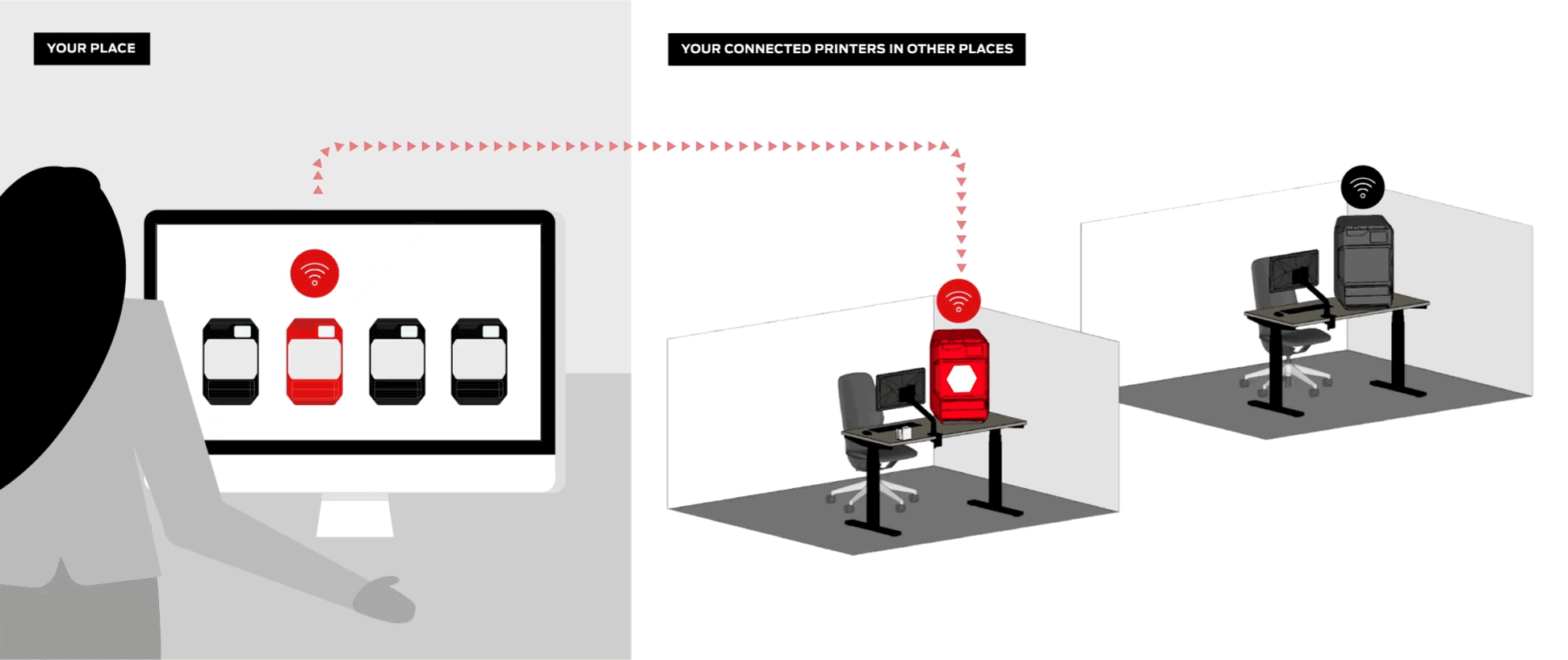
Efficiently manage your 3D printers, queue up student projects, and even monitor ongoing prints remotely.
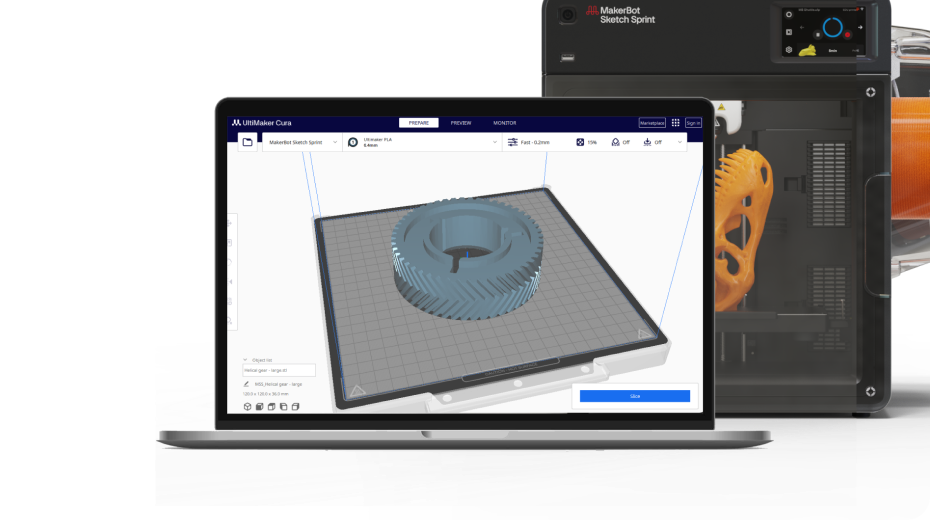
UltiMaker Cura
For advanced users looking to get the most custom control over their 3D printers.
UltiMaker Digital Factory
Digital Factory is an all-in-one 3D printing platform for managing student submissions, printers, and projects from any device
-
Training
Back
Training
Tailored certifications that will help you and your students become experts in 3D printing.
Explore certification -
Resources
Back
Resources
Free access to hundreds of 3D printing lesson plans to help teach a range of subjects.
Browse all blogs and webinarsMakerBot Educator’s Guidebook
This guide has become the ultimate 3D printing textbook for students and educators.
Thingiverse Education Community
Browse hundreds of 3D printing ideas that help engage students of any subject.
MakerBot Grant
The MakerBot Gives Back Grant Program is dedicated to helping K–12 educators bring 3D printing into the classroom
-
Support
Back
Support
Visit our support site for setup videos, how-to guides, FAQs, and technical expertise from our support team.
Support site